Evolution and Importance of Blood Pressure Monitors: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In the realm of healthcare technology, few devices have had as significant an impact on preventive care as blood pressure monitors. These unassuming devices play a crucial role in monitoring and managing cardiovascular health, allowing individuals and healthcare professionals alike to make informed decisions about their well-being. This comprehensive guide delves into the evolution, types, usage, and importance of blood pressure monitors in modern healthcare.
Understanding Blood Pressure
Before delving into the intricacies of blood pressure monitors, it’s essential to grasp the concept of blood pressure itself. Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by blood against the walls of arteries as the heart pumps it around the body. It’s measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed as two values: systolic pressure (the higher number) and diastolic pressure (the lower number). The systolic pressure represents the force when the heart contracts, while diastolic pressure reflects the pressure when the heart rests between beats.
Evolution of Blood Pressure Monitoring
The history of blood pressure monitoring dates back to the 19th century when the Italian physician Scipione Riva-Rocci introduced the first practical method for measuring blood pressure using a mercury manometer and an inflatable cuff. This pioneering technique laid the foundation for subsequent advancements in blood pressure monitoring technology.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer
The aneroid sphygmomanometer, developed in the early 20th century, marked a significant leap forward. This device replaced the mercury manometer with a mechanical gauge that responded to changes in pressure. It became a staple in medical practices and homes alike, offering a more portable and user-friendly option for blood pressure measurement.
Digital Blood Pressure Monitors
The late 20th century witnessed the emergence of digital blood pressure monitors. These devices automated the process, providing digital readings of systolic and diastolic pressure. The introduction of digital monitors made blood pressure measurement even more accessible to individuals, enabling them to monitor their readings with ease.
Types of Blood Pressure Monitors
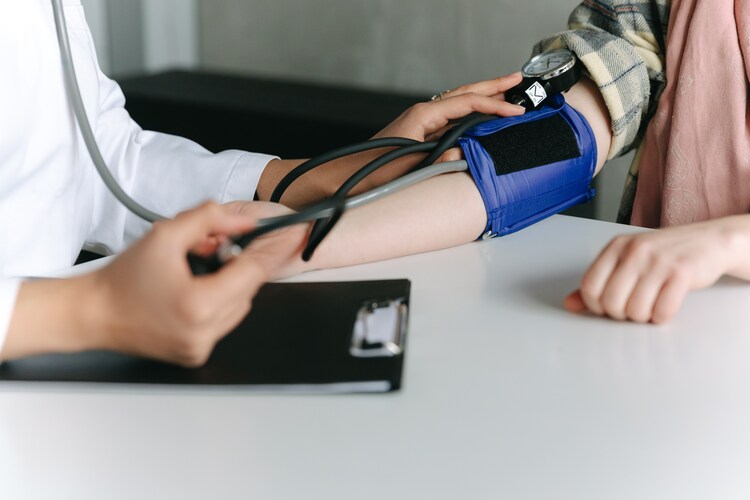
Upper Arm Monitors: These are the traditional type of blood pressure monitors that use an inflatable cuff wrapped around the upper arm. They provide accurate readings and are commonly used in medical settings.
Wrist Monitors: Worn like a wristwatch, these monitors are compact and convenient. However, they might be less accurate than upper arm monitors due to their placement.
Finger Monitors: These portable devices are less common and may not be as accurate as upper arm or wrist monitors. They are generally used in special cases where traditional monitoring is challenging.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitors: These monitors are worn by the patient for an extended period, usually 24 hours. They provide a comprehensive profile of blood pressure changes throughout the day and night, offering valuable insights into a person’s overall cardiovascular health.
Importance of Blood Pressure Monitors
Early Detection of Hypertension: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a silent but dangerous condition that can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other complications. Regular monitoring allows for the early detection of elevated blood pressure, enabling timely intervention and lifestyle adjustments.
Personalized Healthcare: Blood pressure monitors empower individuals to take charge of their health. By tracking their blood pressure regularly, individuals can make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication in consultation with healthcare professionals.
Monitoring Treatment Efficacy: For individuals already diagnosed with hypertension, blood pressure monitors help track the effectiveness of prescribed medications and lifestyle changes. This feedback is vital for doctors to adjust treatment plans as needed.
White Coat Syndrome: Some individuals experience elevated blood pressure in medical settings due to anxiety—a phenomenon known as white coat syndrome. Home blood pressure monitoring provides a more accurate representation of an individual’s typical blood pressure outside of clinical environments.
Preventive Care: Blood pressure monitors play a crucial role in preventive healthcare. By identifying risk factors early, healthcare providers can work with patients to reduce the likelihood of cardiovascular diseases and related complications.
Proper Usage and Tips
Choose the Right Monitor: Select a blood pressure monitor based on accuracy, ease of use, and your specific needs. Consult your healthcare provider for recommendations.
Follow Guidelines: Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for correct cuff placement, body position, and usage. Consistency is key to accurate readings.
Regular Monitoring: For individuals with hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions, monitor your blood pressure as advised by your healthcare provider. Regular monitoring helps in tracking trends and adjustments.
Avoid Caffeine and Smoking: Before taking a reading, refrain from caffeine consumption and smoking, as they can temporarily raise blood pressure levels.
Relaxation and Rest: Sit quietly for a few minutes before taking a measurement. Ensure that your back is supported and your feet are flat on the ground. Avoid talking during the reading.
Conclusion
Blood pressure monitors have come a long way from their mercury-filled origins to the digital devices we use today. Their evolution has democratized cardiovascular health monitoring, enabling individuals to actively participate in their well-being. By providing timely and accurate information, blood pressure monitors empower individuals to make informed decisions about their lifestyle, treatment plans, and overall health. In an era where preventive care is gaining paramount importance, these unassuming devices play a vital role in safeguarding our cardiovascular health and enhancing our quality of life.



































